8.2 KiB
| id | title |
|---|---|
| index | Quickstart |
In this quickstart, we will download Druid and set it up on a single machine. The cluster will be ready to load data after completing this initial setup.
Before beginning the quickstart, it is helpful to read the general Druid overview and the ingestion overview, as the tutorials will refer to concepts discussed on those pages.
Prerequisites
Software
You will need:
- Java 8 (8u92+)
- Linux, Mac OS X, or other Unix-like OS (Windows is not supported)
Hardware
Druid includes several example single-server configurations, along with scripts to start the Druid processes using these configurations.
If you're running on a small machine such as a laptop for a quick evaluation, the micro-quickstart configuration is
a good choice, sized for a 4CPU/16GB RAM environment.
If you plan to use the single-machine deployment for further evaluation beyond the tutorials, we recommend a larger
configuration than micro-quickstart.
Getting started
Download the #{DRUIDVERSION} release.
Extract Druid by running the following commands in your terminal:
tar -xzf apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION}-bin.tar.gz
cd apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION}
In the package, you should find:
DISCLAIMER,LICENSE, andNOTICEfilesbin/*- scripts useful for this quickstartconf/*- example configurations for single-server and clustered setupextensions/*- core Druid extensionshadoop-dependencies/*- Druid Hadoop dependencieslib/*- libraries and dependencies for core Druidquickstart/*- configuration files, sample data, and other files for the quickstart tutorials
Download Zookeeper
Druid has a dependency on Apache ZooKeeper for distributed coordination. You'll need to download and run Zookeeper.
In the package root, run the following commands:
curl https://archive.apache.org/dist/zookeeper/zookeeper-3.4.14/zookeeper-3.4.14.tar.gz -o zookeeper-3.4.14.tar.gz
tar -xzf zookeeper-3.4.14.tar.gz
mv zookeeper-3.4.14 zk
The startup scripts for the tutorial will expect the contents of the Zookeeper tarball to be located at zk under the
apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION} package root.
Start up Druid services
The following commands will assume that you are using the micro-quickstart single-machine configuration. If you are
using a different configuration, the bin directory has equivalent scripts for each configuration, such as
bin/start-single-server-small.
From the apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION} package root, run the following command:
./bin/start-micro-quickstart
This will bring up instances of Zookeeper and the Druid services, all running on the local machine, e.g.:
$ ./bin/start-micro-quickstart
[Fri May 3 11:40:50 2019] Running command[zk], logging to[/apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION}/var/sv/zk.log]: bin/run-zk conf
[Fri May 3 11:40:50 2019] Running command[coordinator-overlord], logging to[/apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION}/var/sv/coordinator-overlord.log]: bin/run-druid coordinator-overlord conf/druid/single-server/micro-quickstart
[Fri May 3 11:40:50 2019] Running command[broker], logging to[/apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION}/var/sv/broker.log]: bin/run-druid broker conf/druid/single-server/micro-quickstart
[Fri May 3 11:40:50 2019] Running command[router], logging to[/apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION}/var/sv/router.log]: bin/run-druid router conf/druid/single-server/micro-quickstart
[Fri May 3 11:40:50 2019] Running command[historical], logging to[/apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION}/var/sv/historical.log]: bin/run-druid historical conf/druid/single-server/micro-quickstart
[Fri May 3 11:40:50 2019] Running command[middleManager], logging to[/apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION}/var/sv/middleManager.log]: bin/run-druid middleManager conf/druid/single-server/micro-quickstart
All persistent state such as the cluster metadata store and segments for the services will be kept in the var directory under the apache-druid-#{DRUIDVERSION} package root. Logs for the services are located at var/sv.
Later on, if you'd like to stop the services, CTRL-C to exit the bin/start-micro-quickstart script, which will terminate the Druid processes.
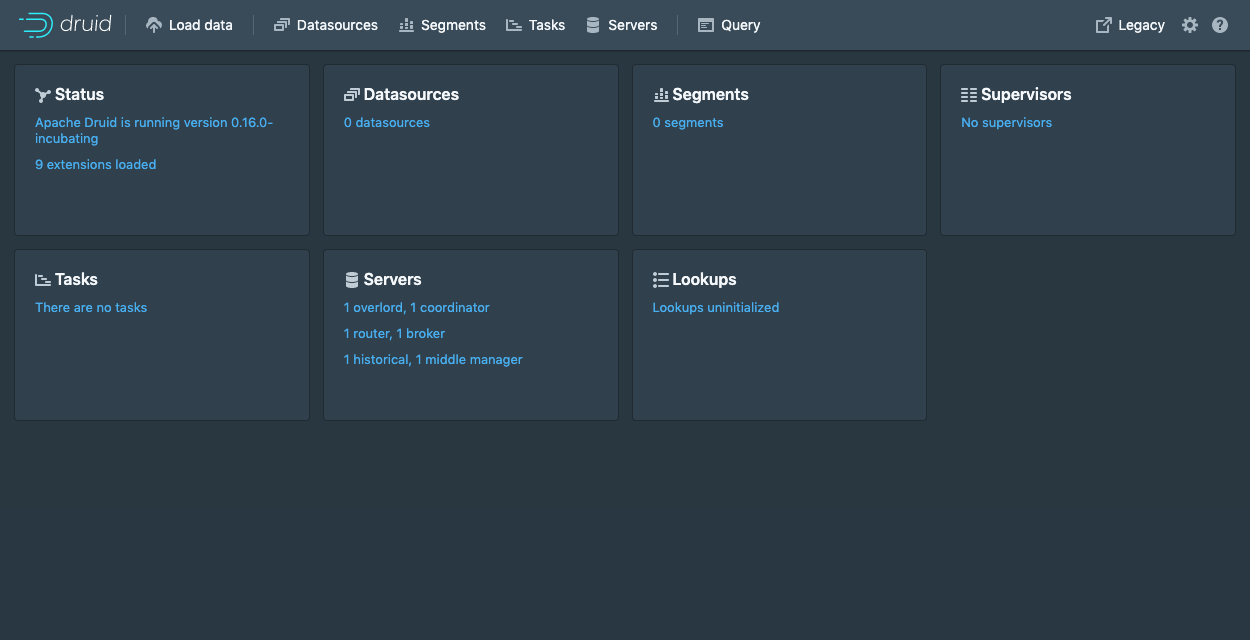
Once the cluster has started, you can navigate to http://localhost:8888. The Druid router process, which serves the Druid console, resides at this address.
It takes a few seconds for all the Druid processes to fully start up. If you open the console immediately after starting the services, you may see some errors that you can safely ignore.
Loading data
Tutorial dataset
For the following data loading tutorials, we have included a sample data file containing Wikipedia page edit events that occurred on 2015-09-12.
This sample data is located at quickstart/tutorial/wikiticker-2015-09-12-sampled.json.gz from the Druid package root.
The page edit events are stored as JSON objects in a text file.
The sample data has the following columns, and an example event is shown below:
- added
- channel
- cityName
- comment
- countryIsoCode
- countryName
- deleted
- delta
- isAnonymous
- isMinor
- isNew
- isRobot
- isUnpatrolled
- metroCode
- namespace
- page
- regionIsoCode
- regionName
- user
{
"timestamp":"2015-09-12T20:03:45.018Z",
"channel":"#en.wikipedia",
"namespace":"Main",
"page":"Spider-Man's powers and equipment",
"user":"foobar",
"comment":"/* Artificial web-shooters */",
"cityName":"New York",
"regionName":"New York",
"regionIsoCode":"NY",
"countryName":"United States",
"countryIsoCode":"US",
"isAnonymous":false,
"isNew":false,
"isMinor":false,
"isRobot":false,
"isUnpatrolled":false,
"added":99,
"delta":99,
"deleted":0,
}
Data loading tutorials
The following tutorials demonstrate various methods of loading data into Druid, including both batch and streaming use cases.
All tutorials assume that you are using the micro-quickstart single-machine configuration mentioned above.
- Loading a file - this tutorial demonstrates how to perform a batch file load, using Druid's native batch ingestion.
- Loading stream data from Apache Kafka - this tutorial demonstrates how to load streaming data from a Kafka topic.
- Loading a file using Apache Hadoop - this tutorial demonstrates how to perform a batch file load, using a remote Hadoop cluster.
- Writing your own ingestion spec - this tutorial demonstrates how to write a new ingestion spec and use it to load data.
Resetting cluster state
If you want a clean start after stopping the services, delete the var directory and run the bin/start-micro-quickstart script again.
Once every service has started, you are now ready to load data.
Resetting Kafka
If you completed Tutorial: Loading stream data from Kafka and wish to reset the cluster state, you should additionally clear out any Kafka state.
Shut down the Kafka broker with CTRL-C before stopping Zookeeper and the Druid services, and then delete the Kafka log directory at /tmp/kafka-logs:
rm -rf /tmp/kafka-logs