7.3 KiB
| id | title |
|---|---|
| tutorial-batch-native | Load data with native batch ingestion |
This topic shows you how to load and query data files in Apache Druid using its native batch ingestion feature.
Prerequisites
Install Druid, start up Druid services, and open the web console as described in the Druid quickstart.
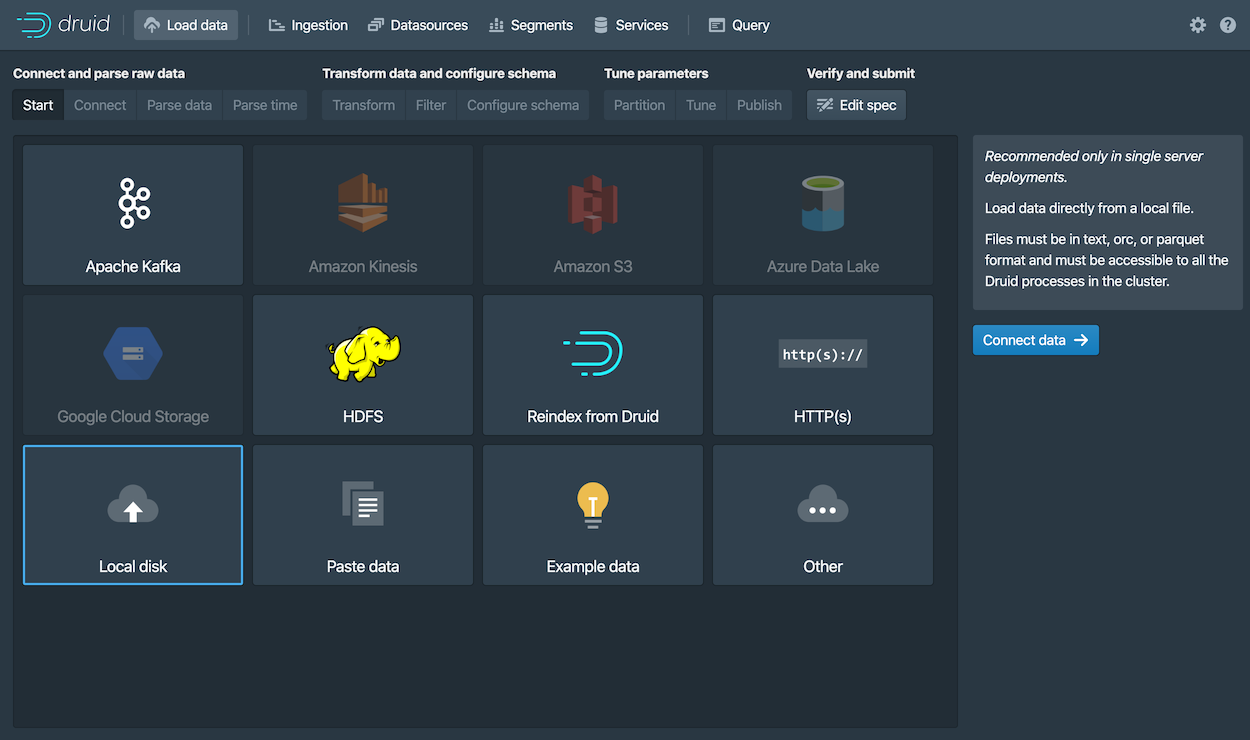
Load data
Ingestion specs define the schema of the data Druid reads and stores. You can write ingestion specs by hand or using the data loader, as we'll do here to perform batch file loading with Druid's native batch ingestion.
The Druid distribution bundles sample data we can use. The sample data located in quickstart/tutorial/wikiticker-2015-09-12-sampled.json.gz
in the Druid root directory represents Wikipedia page edits for a given day.
-
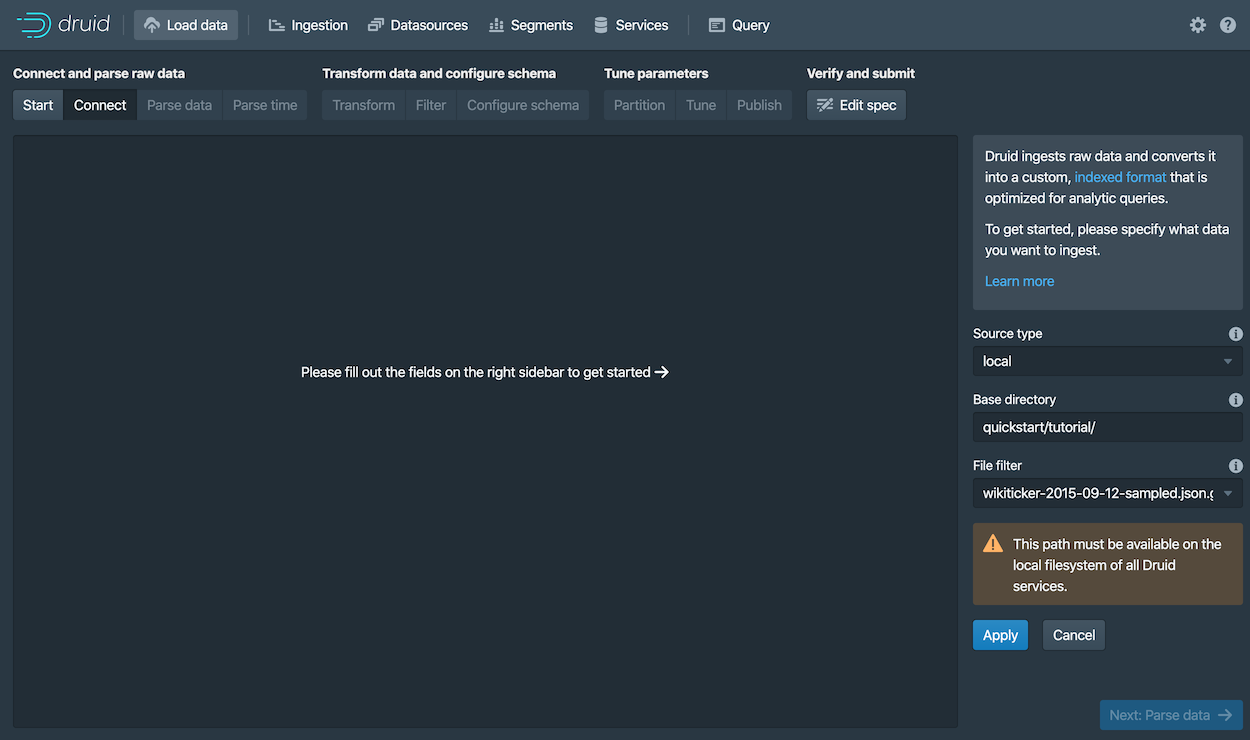
Select the Local disk tile and then click Connect data.
-
Enter the following values:
-
Base directory:
quickstart/tutorial/ -
File filter:
wikiticker-2015-09-12-sampled.json.gz
Entering the base directory and wildcard file filter separately, as afforded by the UI, allows you to specify multiple files for ingestion at once.
-
-
Click Apply.
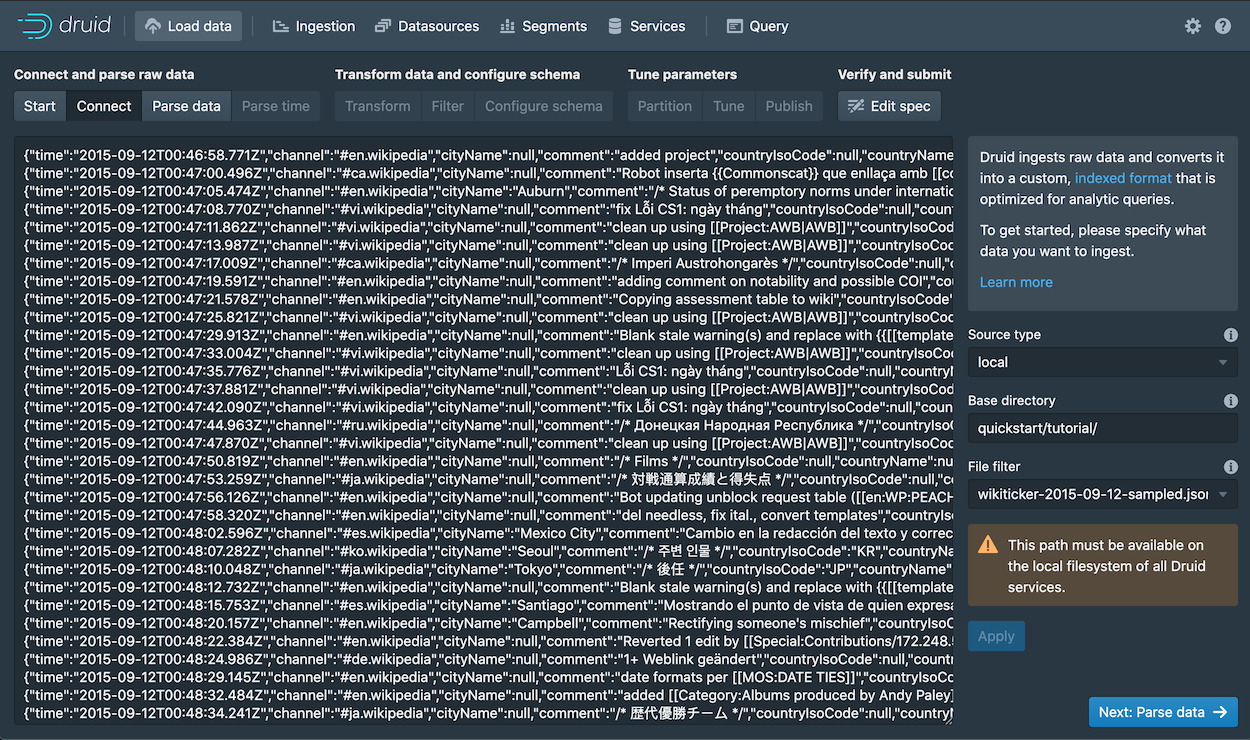
The data loader displays the raw data, giving you a chance to verify that the data appears as expected.
Notice that your position in the sequence of steps to load data, Connect in our case, appears at the top of the console, as shown below. You can click other steps to move forward or backward in the sequence at any time.
-
Click Next: Parse data.
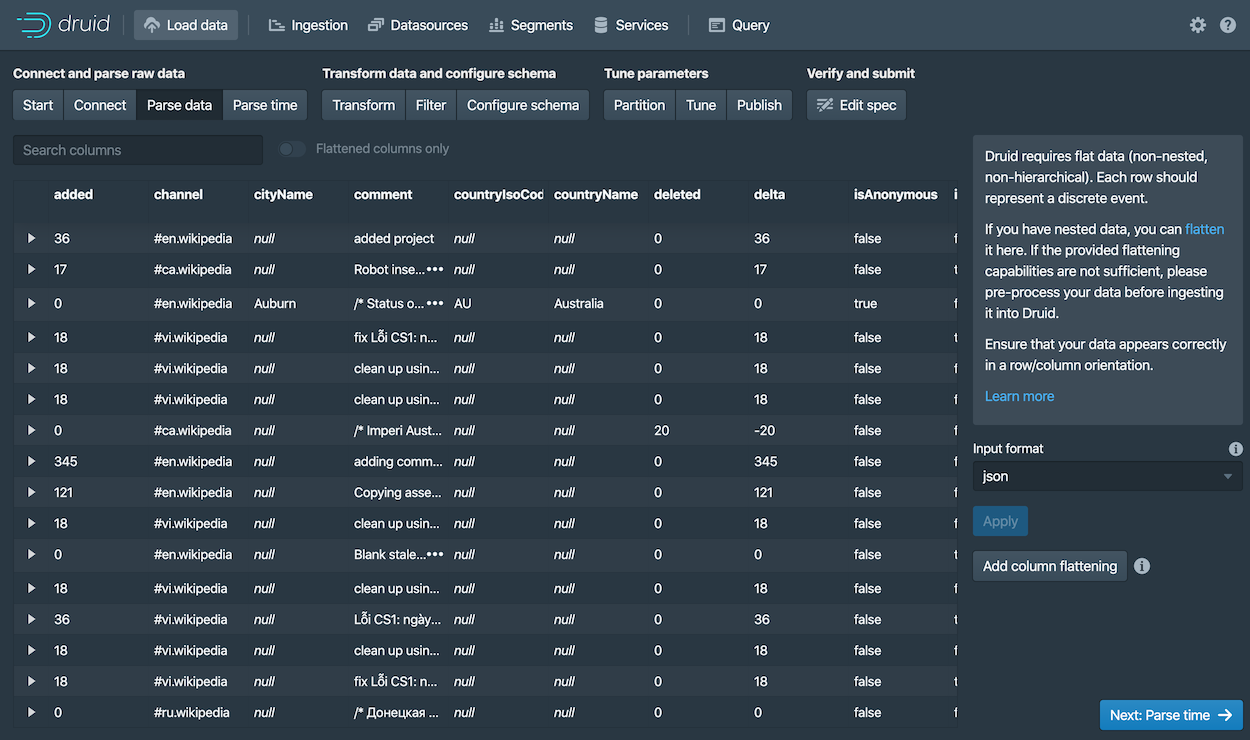
The data loader tries to determine the parser appropriate for the data format automatically. In this case it identifies the data format as
json, as shown in the Input format field at the bottom right.Feel free to select other Input format options to get a sense of their configuration settings and how Druid parses other types of data.
-
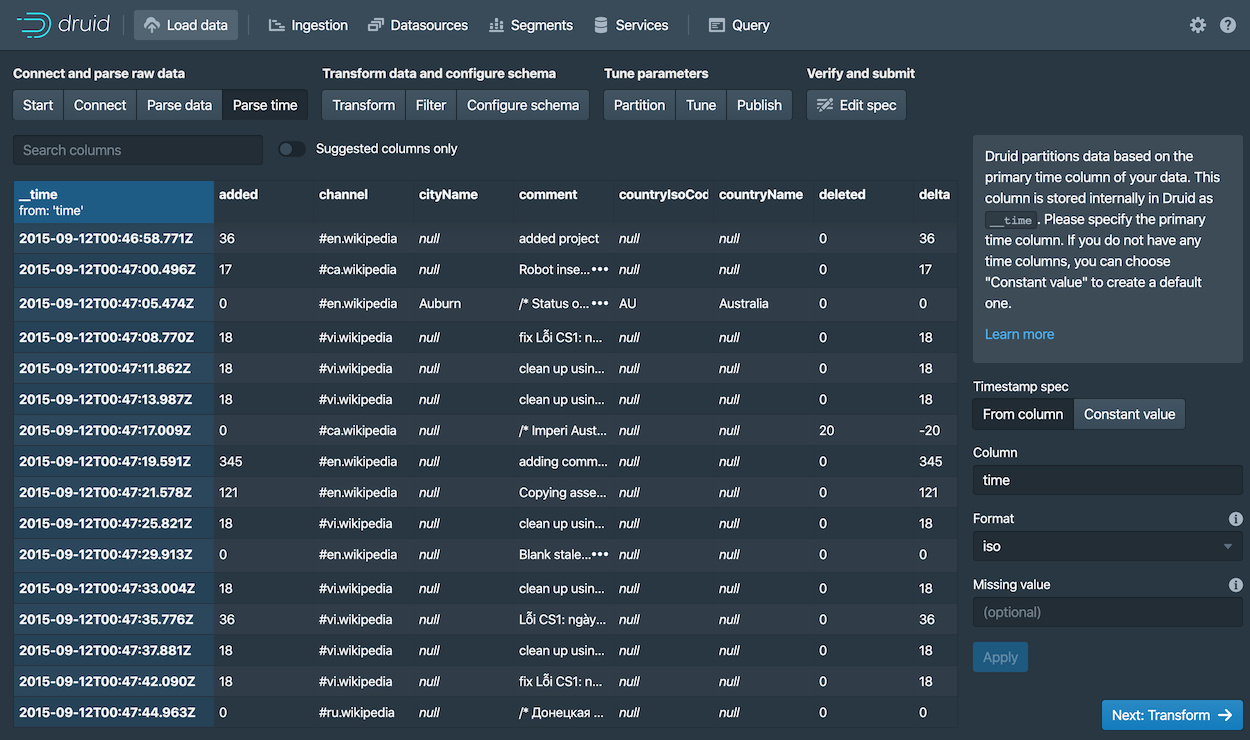
With the JSON parser selected, click Next: Parse time. The Parse time settings are where you view and adjust the primary timestamp column for the data.
Druid requires data to have a primary timestamp column (internally stored in a column called
__time). If you do not have a timestamp in your data, selectConstant value. In our example, the data loader determines that thetimecolumn is the only candidate that can be used as the primary time column. -
Click Next: Transform, Next: Filter, and then Next: Configure schema, skipping a few steps.
You do not need to adjust transformation or filtering settings, as applying ingestion time transforms and filters are out of scope for this tutorial.
-
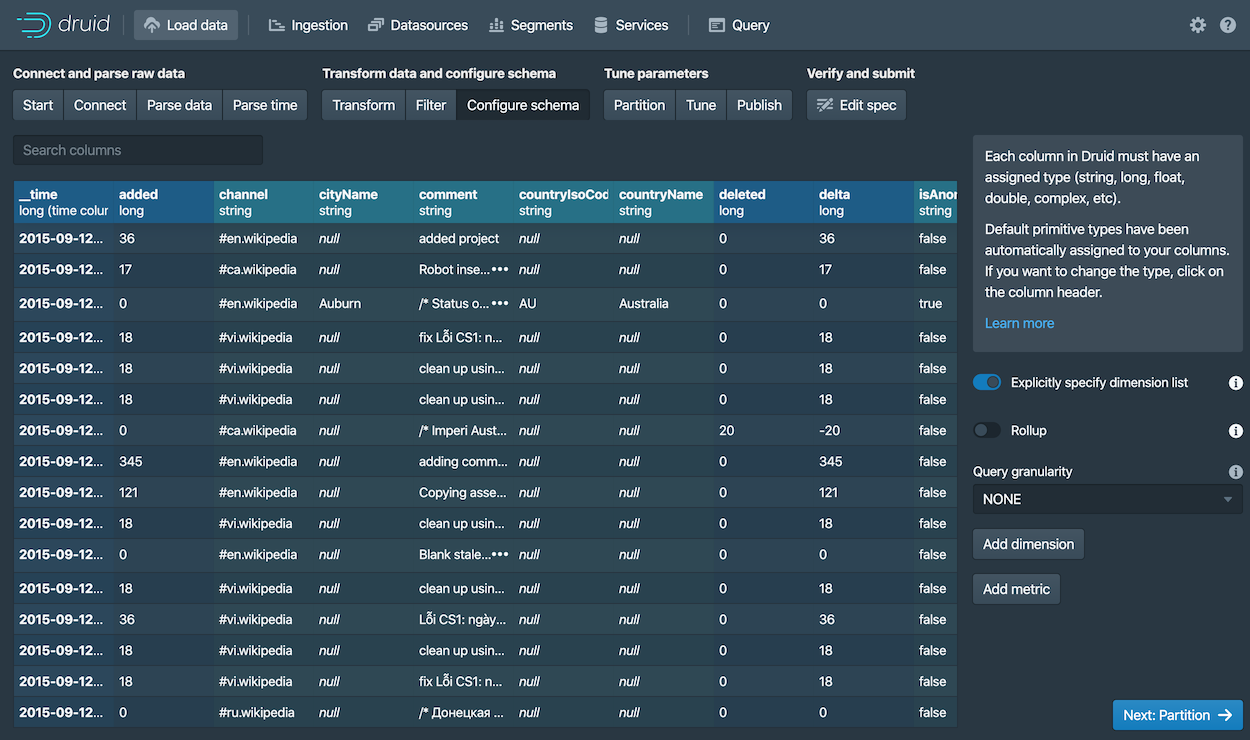
The Configure schema settings are where you configure what dimensions and metrics are ingested. The outcome of this configuration represents exactly how the data will appear in Druid after ingestion.
Since our dataset is very small, you can turn off rollup by unsetting the Rollup switch and confirming the change when prompted.
-
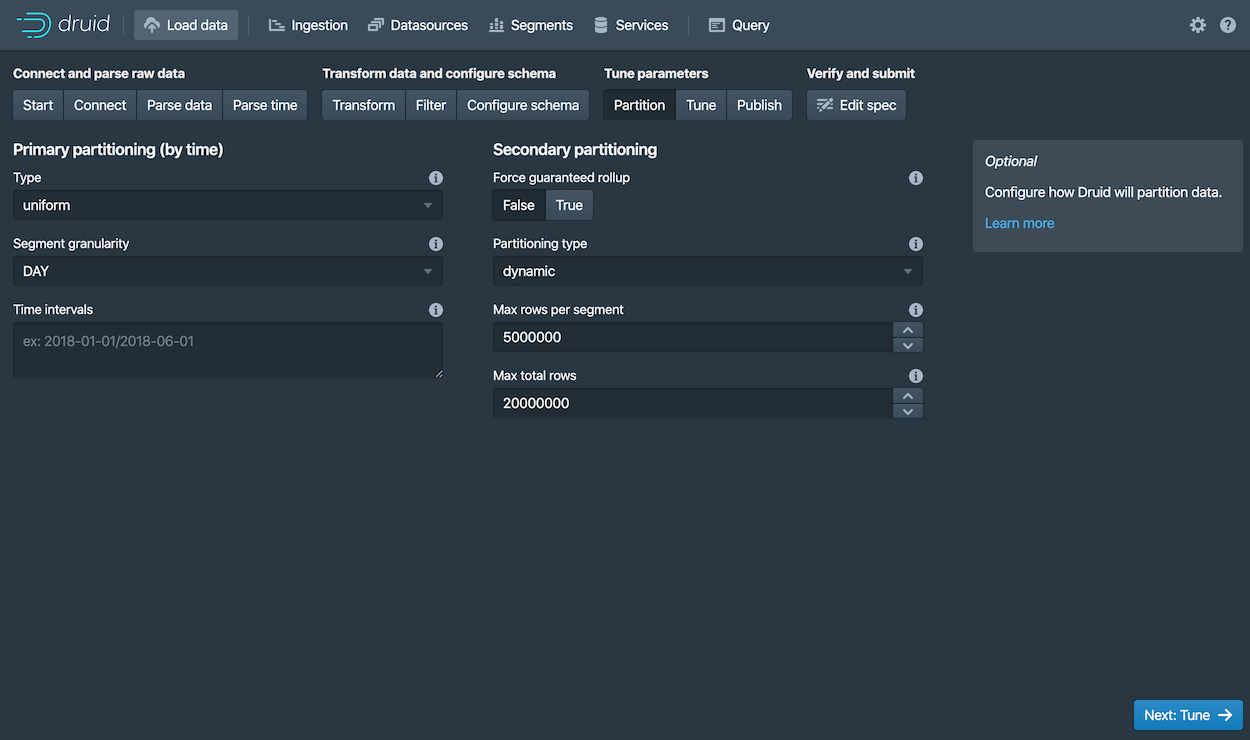
Click Next: Partition to configure how the data will be split into segments. In this case, choose
DAYas the Segment granularity.Since this is a small dataset, we can have just a single segment, which is what selecting
DAYas the segment granularity gives us. -
Click Next: Tune and Next: Publish.
-
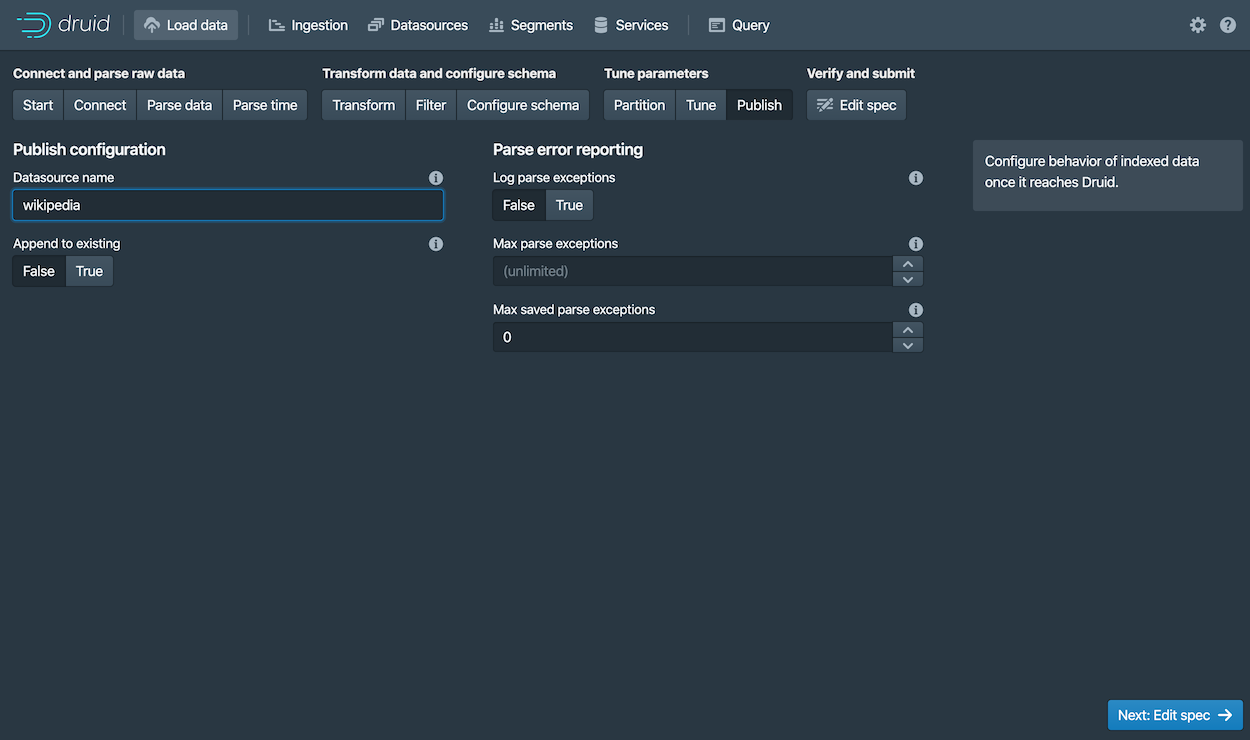
The Publish settings are where you specify the datasource name in Druid. Let's change the default name from
wikiticker-2015-09-12-sampledtowikipedia. -
Click Next: Edit spec to review the ingestion spec we've constructed with the data loader.
Feel free to go back and change settings from previous steps to see how doing so updates the spec. Similarly, you can edit the spec directly and see it reflected in the previous steps.
For other ways to load ingestion specs in Druid, see Tutorial: Loading a file.
-
Once you are satisfied with the spec, click Submit.
The new task for our wikipedia datasource now appears in the Ingestion view.
The task may take a minute or two to complete. When done, the task status should be "SUCCESS", with the duration of the task indicated. Note that the view is set to automatically refresh, so you do not need to refresh the browser to see the status change.
A successful task means that one or more segments have been built and are now picked up by our data servers.
Query the data
You can now see the data as a datasource in the console and try out a query, as follows:
-
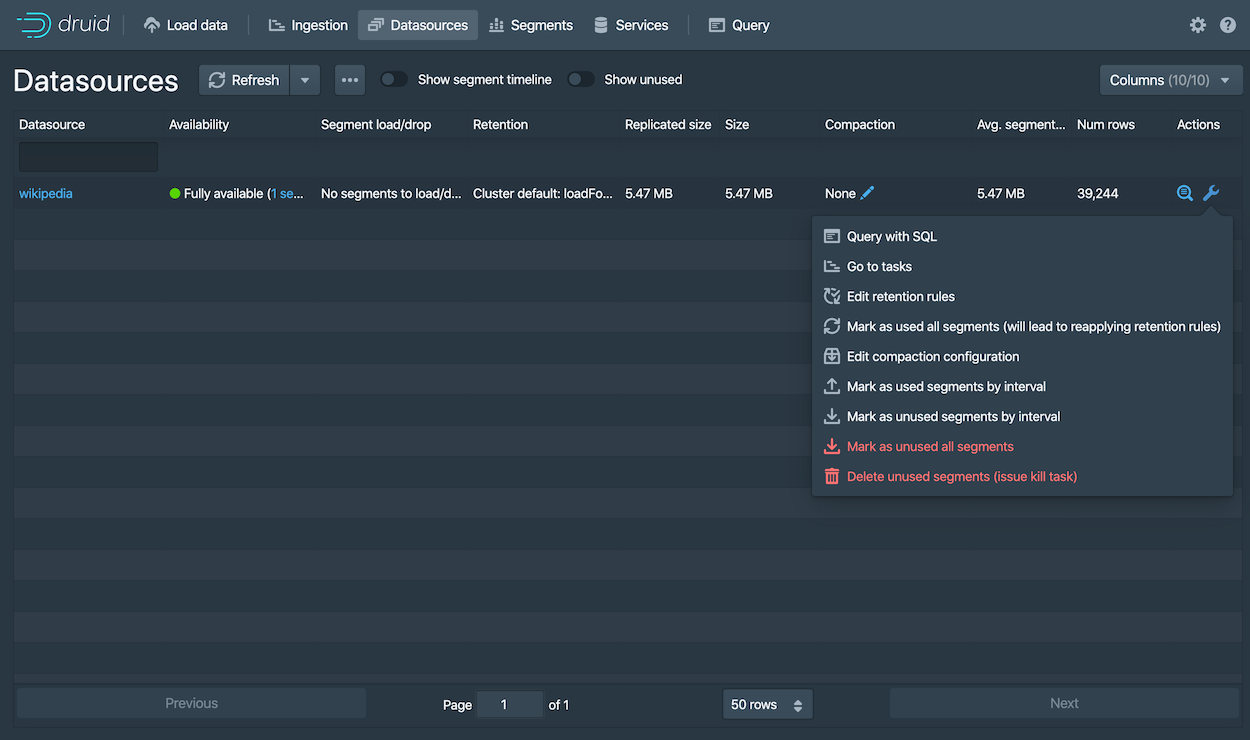
Click Datasources from the console header.
If the wikipedia datasource doesn't appear, wait a few moments for the segment to finish loading. A datasource is queryable once it is shown to be "Fully available" in the Availability column.
-
When the datasource is available, open the Actions menu (
 ) for that
datasource and choose Query with SQL.
) for that
datasource and choose Query with SQL.Notice the other actions you can perform for a datasource, including configuring retention rules, compaction, and more.
-
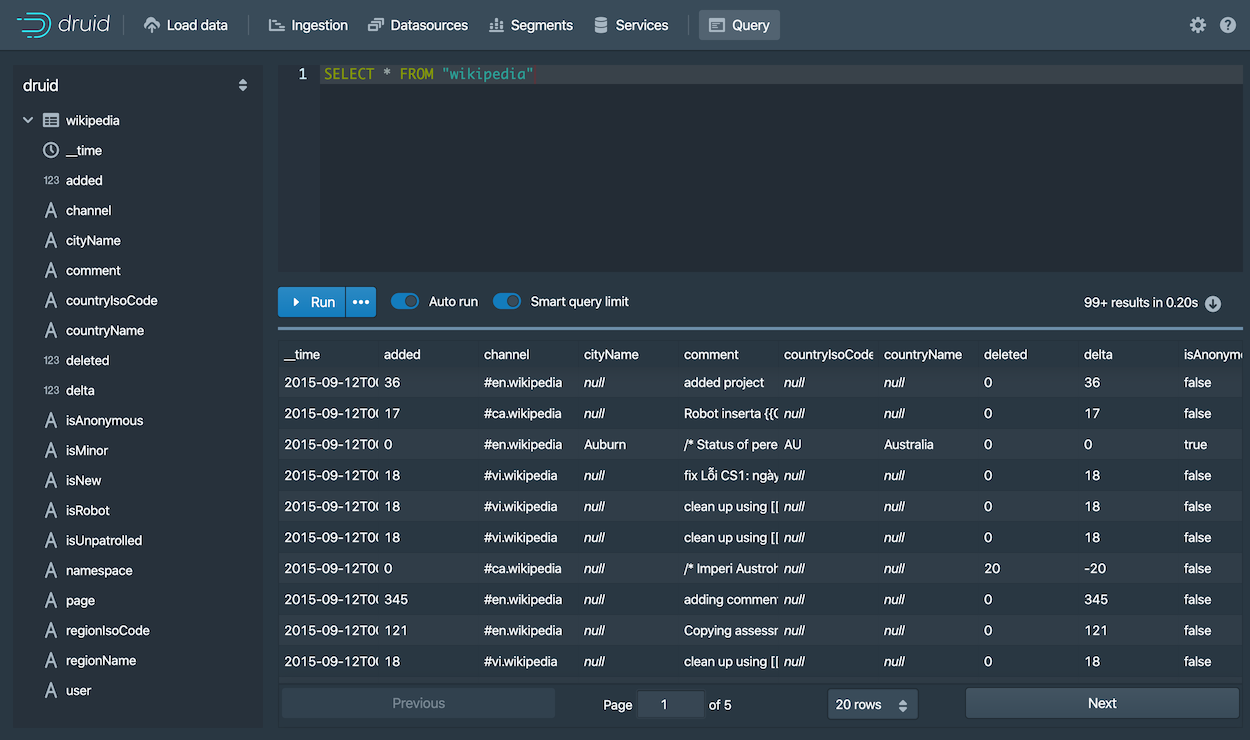
Run the prepopulated query,
SELECT * FROM "wikipedia"to see the results.