5.9 KiB
| description | keywords | title | redirect_from | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Docker Hub Teams & Organizations | Docker, docker, registry, teams, organizations, plans, Dockerfile, Docker Hub, docs, documentation | Teams and Organizations |
|
Docker Hub organizations let you create teams so you can give your team access to shared image repositories.
- Organizations are collections of teams and repositories that can be managed together.
- Teams are groups of Docker Hub users that belong to an organization.
Note: in Docker Hub, users cannot belong directly to an organization. They belong only to teams within an organization.
Working with organizations
Create an organization
-
Start by clicking on Organizations in Docker Hub.
-
Click on Create Organization.
-
Provide information about your organization.
You've created an organization. You'll see you have a team, the owners team with a single member (you!).
The owners team
The owners team is a special team that has full access to all repositories in the organization.
Members of this team can:
- Manage organization settings and billing
- Create a team and modify the membership of any team
- Access and modify any repository belonging to the organization
Access an organization
You can't directly log into an organization. This is especially important to note if you create an organization by converting a user account, as conversion means you lose the ability to log into that "account", since it no longer exists.
To access an organization:
-
Log into Docker Hub with a user account that is a member of any team in the organization.
If you want access to organization settings, this account has to be part of the owners team.
-
Click Organizations in the top navigation bar, then choose your organization from the list.
If you don't see the organization, then you are neither a member or an owner of it. An organization administrator will need to add you as a member of the organization team.
Working with teams and members
Create a team
-
Go to Organizations in Docker Hub, and select your organization.
-
Open the Teams tab and click Create Team.
-
Fill out your team's information and click Create.
Add a member to a team
You can add a member to a team in one of two ways.
If the user isn't in your organization:
-
Go to Organizations in Docker Hub, and select your organization.
-
Click Add Member.
-
Enter the user's Docker ID or email, and select a team from the drop-down list.
-
Click Add to confirm.
If the user already belongs to another team in the organization:
-
Open the team's page in Docker Hub: Organizations > Your Organization > Teams > Your Team Name
-
Click Add user.
-
Enter the user's Docker ID or email to add them to the team.
Note
: You are not automatically added to teams created by your organization.
Remove team members
To remove a member from all teams in an organization:
-
Go to Organizations in Docker Hub, and select your organization. The Organizations page lists all team members.
-
Click the x next to a member’s name to remove them from all the teams in the organization.
-
When prompted, click Remove to confirm the removal.
To remove a member from a specific team:
-
Go to Organizations in Docker Hub, and select your organization.
-
Click on the Teams tab and select the team from the list.
-
Click the x next to the user's name to remove them from the team.
-
When prompted, click Remove to confirm the removal. to confirm the removal.
Give a team access to a repository
-
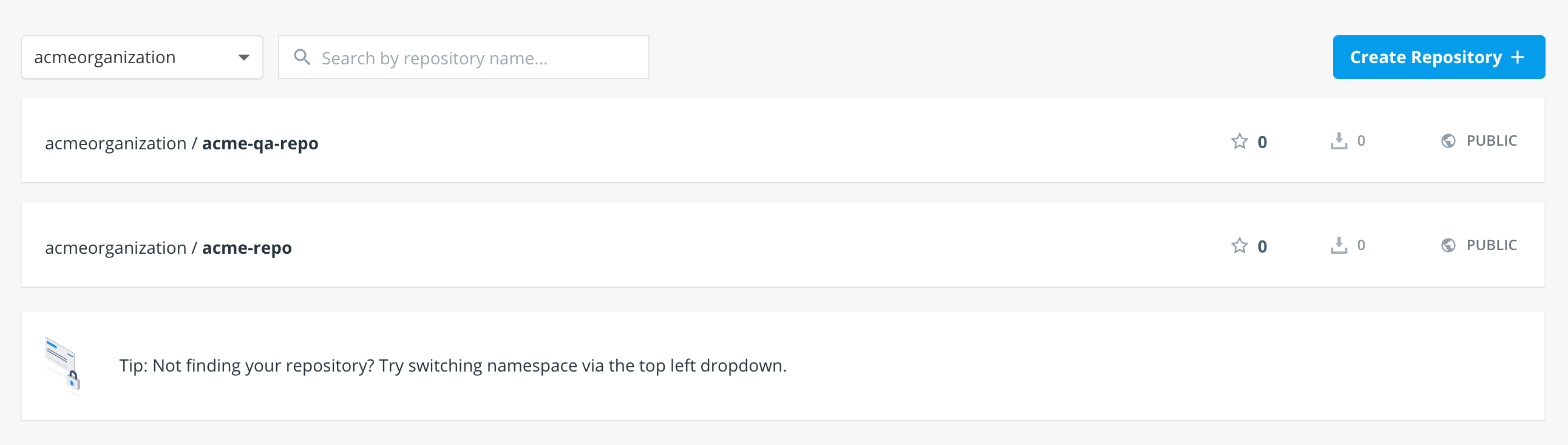
Visit the repository list on Docker Hub by clicking on Repositories.
-
Select your organization in the namespace dropdown list.
-
Click the repository you'd like to edit.
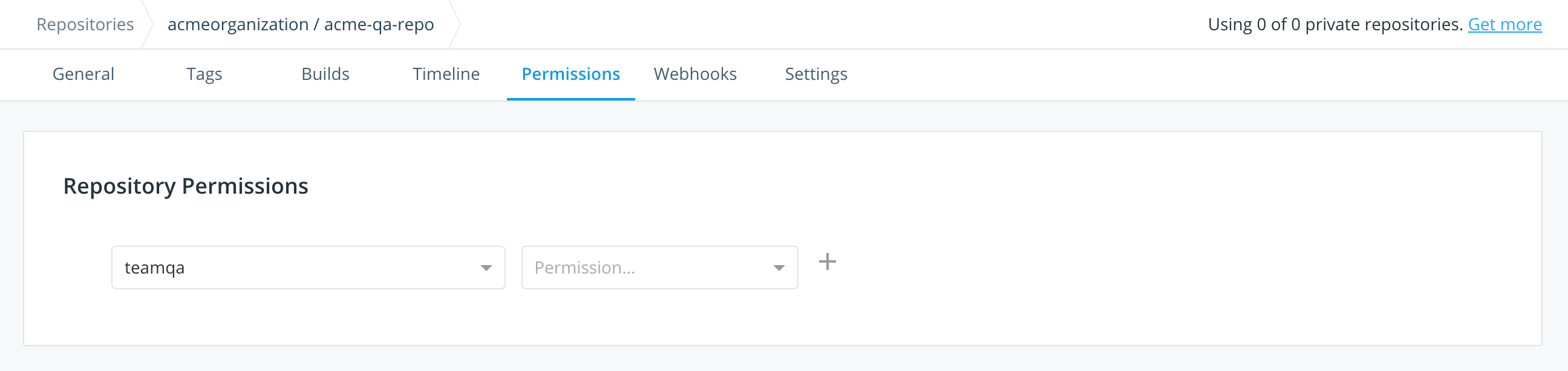
-
Click the Permissions tab.
-
Select the team, the permissions level, and click + to save.
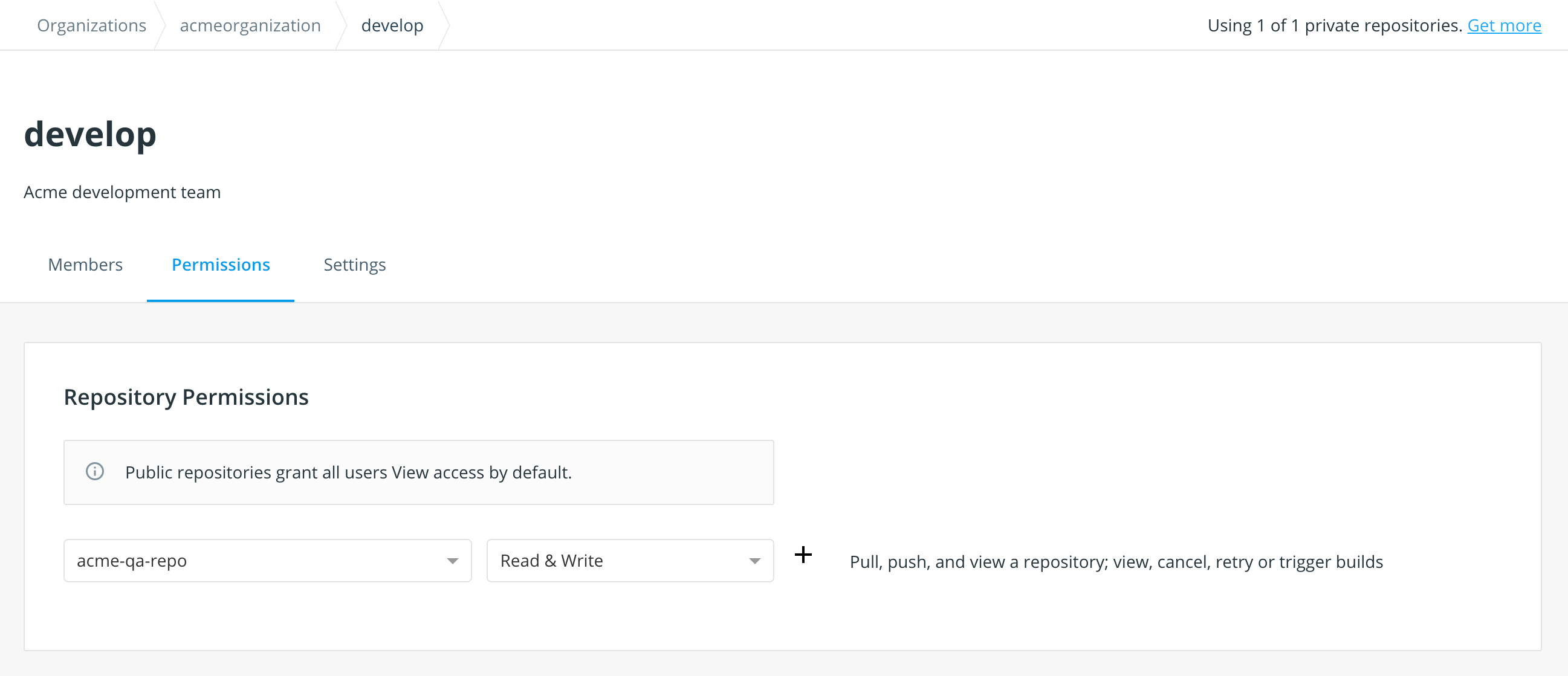
View a team's permissions for all repositories
To view a team's permissions over all repos:
-
Open Organizations > Your Organization > Teams > Team Name.
-
Click on the Permissions tab, where you can view the repositories this team can access.
You can also edit repository permissions from this tab.
Permissions reference
Permissions are cumulative. For example, if you have Write permissions, you automatically have Read permissions:
Readaccess allows users to view, search, and pull a private repository in the same way as they can a public repository.Writeaccess allows users to push to repositories on Docker Hub.Adminaccess allows users to modify the repositories "Description", "Collaborators" rights, "Public/Private" visibility, and "Delete".
Note
: A User who has not yet verified their email address only has
Readaccess to the repository, regardless of the rights their team membership has given them.